Getting to know EEG artifacts and how to handle them in BrainVision Analyzer 2
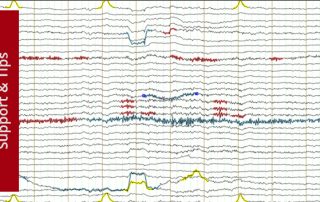
In this article we present a collection of common EEG artifacts with their characteristics and pictures to facilitate their identification, and various tools offered by BrainVision Analyzer 2 for artifact detection, rejection, and removal. Towards the end we make some suggestions for devising an overall artifact handling strategy.